The last few years have been a time of change for the auto logistics industry. While the economy continued to fluctuate, dealer inventory levels managed to stabilize. At the same time, customer purchasing habits shifted, creating a greater demand for used vehicles over new ones. To keep up with these changes and ensure competitive pay for carriers, auto logistics providers are embracing new strategies and exploring emerging technologies.
Carrier Pay Cycle: A Return to Normal Patterns
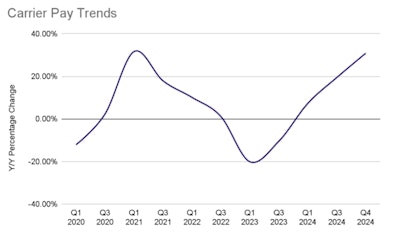
After a period of low pay due to supply chain difficulties and economic fluctuations, carrier pay rates slowly increased as demand stabilized and the market regained balance in 2024.
Ship.Cars’ internal carrier pay report shows the percentage of carrier pay change year over year. The trend line indicates that the industry is entering a deflationary period, which bodes well for carrier pay.
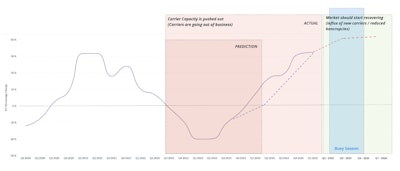
This trend is expected to continue as increased demand, operational cost pressures, and industry consolidation continue to push pay rates higher. Based on the current economic factors and consumer buying habits, increased carrier rates will continue to rise through the coming year and likely peak by late 2025 or early 2026.
The following chart shows the year-over-year carrier pay changes with an overlay of our forecasts for 2024 and 2025.
Shifting Customer Demand and Economic Factors
New consumer buying habits combined with stable dealership inventories have positively impacted the auto industry, including carriers. With consumer demand shifting from new to used vehicles, auto transport remains an essential service in the industry. Furthermore, a growing interest in electric and hybrid vehicles presents new opportunities for carriers to expand their services.
Strategic Fleet Adjustments for EV Transportation
Globally, an estimated 85 million EVs are expected to be on the road in 2025, representing a 33% increase from 2024. EV production will drive new logistics needs, benefitting carriers that have the skills and equipment to handle those vehicles. With their heavier battery weight and unique safety requirements, electric and hybrid vehicles need special load configurations and handling.
Because EVs and hybrid vehicles are heavier than standard vehicles, this means that carriers may need to limit their load capacity. If transporting smaller loads, EV shippers will need to book more shipments to move their inventories. We anticipate that carriers will continue updating their fleets to accommodate EV requirements, positioning themselves to meet the growing demand from auto manufacturers and dealerships.
Additionally, auto manufacturers that were heavily investing in EVs have shifted some of their production efforts to hybrid vehicles. Hybrid vehicles address concerns that consumers have about charging and infrastructure limitations in rural areas, and have seen a steady increase in sales alongside their fully electric counterparts. An uptick in hybrid vehicle production and sales contributes to the need for specialized carriers with the capabilities to transport hybrid and electric vehicles.
Carriers Needed to Meet Growing Demand
The auto logistics industry still faces a shortage of drivers. The latest report from the American Trucking Association (ATA) showed that the industry was short approximately 60,000 drivers in 2023 (estimates pending for 2024). While the number is down from 78,000 in 2022 and 81,000 in 2021, a driver shortage will continue to be a problem in the coming year as demand for their services increases.
This shortage has made driver retention a key focus for carriers. One of the leading retention strategies for carriers is competitive pay, as well as enhanced safety measures, and improved work-life balance. To implement these strategies and retain drivers, logistics providers, and carrier companies alike are exploring and investing in new technologies.
Leveraging Technology to Boost Performance and Retain Drivers
One key area of development is AI-powered solutions for vehicle inspections, predictive maintenance, and route optimization. With intelligent, automated technology handling these operations logistics providers will be able to reduce costs and maximize fleet uptime, ultimately leading to better carrier pay.
Ship.Cars has made use of similar technology with its SmartHaul TMS platform. SmartHaul includes a suite of advanced tools and applications to help drivers work smarter. One of the platform’s most powerful tools is Load Scout, a machine learning tool that matches carriers with the best loads. Load Scout uses AI to learn carrier preferences, analyze market trends, and proactively suggest loads so drivers can save time, improve efficiency, and increase revenue.
Another way that AI is being used to boost performance and retain carrier pay has to do with fuel prices. The cost of diesel fuel is a major, ongoing economic factor affecting carrier pay. When fuel prices rise, carriers may face a reduction in profits and pay. To address fluctuating diesel prices in 2025, carriers are adopting dynamic pricing models (powered by AI and smart technology) to account for fuel costs and protect profitability–a strategy that could help stabilize pay for carriers even when fuel prices continue to change. Ship.Cars is already leading the industry with its own internal, automated pricing insights tool. This is one opportunity for automated technologies and AI tools to manage operations and secure competitive wages for carriers.
Looking Ahead: 2025 and Beyond
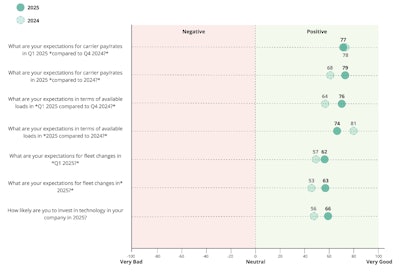
Our annual carrier sentiment survey shows a very positive outlook for the year ahead, consistent with our predictions shown at the beginning of this article. Specifically, the survey indicates positive expectations for carrier pay rates and available loads when comparing Q1 2025 to Q4 2024 and 2025 to 2024. It also indicates expectations for fleet changes and technology investment in 2025.
With inventory levels expected to remain stable, there will be a steady demand for carriers to transport used cars, EVs, and hybrids to/from dealership lots and auctions. The ongoing driver shortage means retention will remain a top priority for carriers. This will incentivize the adoption and integration of new technology and software platforms to help improve operations and meet customer demand.
These new technologies include AI-powered solutions designed to help with vehicle inspections, route optimization, and maintenance to reduce costs and keep fleets running smoothly. Additionally, AI-powered pricing models will assist carriers in stabilizing pay while fuel costs fluctuate.
In conclusion, we expect the automotive industry will navigate traditional challenges while taking advantage of new opportunities for growth. Carriers that are able to adapt with new strategies and invest in emerging tech will be able to position themselves for success.